Complete SEO Guide for Beginners

Do you want to learn SEO but don’t know where to start? This beginner’s guide will teach you everything you need to know about SEO so you can start improving your website’s rankings by yourself! Plus, as a bonus, you can take a short quiz and earn a free SEO certificate!
Chapter-1
SEO Basics
Before diving into specific SEO Guide, let’s first cover the basics: the key terms, definitions, and common questions. Ready? Let’s go!
Chapter navigation
What is SEO? – SEO in a nutshell – SEO vocabulary – FAQs
What is SEO?
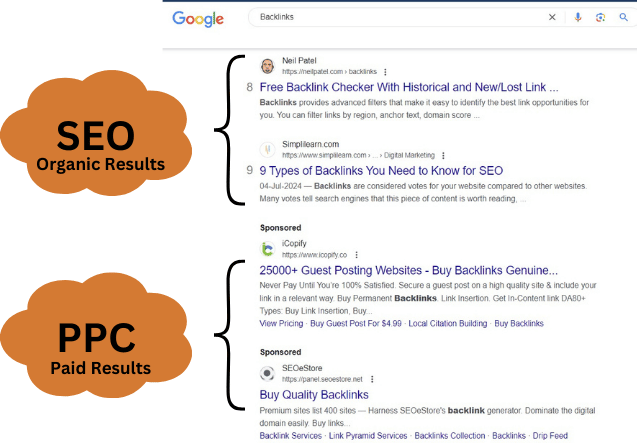
SEO, or search engine optimization, is the process of improving your website so it ranks higher in search results and gets more organic (non-paid) traffic.
SEO has been around since the 1990s when search engines were first created. Today, it’s a crucial marketing strategy and an ever-growing industry.
SEO focuses on organic search results, not paid ads (PPC). Both SEO and PPC fall under Search Engine Marketing.
Search engines are tools that people use to find information online. You want your website to provide the answers they’re looking for. Whether you sell products, offer services, or write a blog, SEO is essential for every website owner.
Simply put: SEO is the work you do to show Google your website is valuable so it ranks higher in search results.
Note: While SEO stands for “search engine optimization,” most of the tips and strategies here focus on Google SEO, as Google dominates the search engine market. However, many of these tips can apply to other search engines as well.
SEO in a Nutshell
You don’t need to understand every factor or algorithm Google uses to rank websites. But you do need to cover the main areas of SEO to succeed.
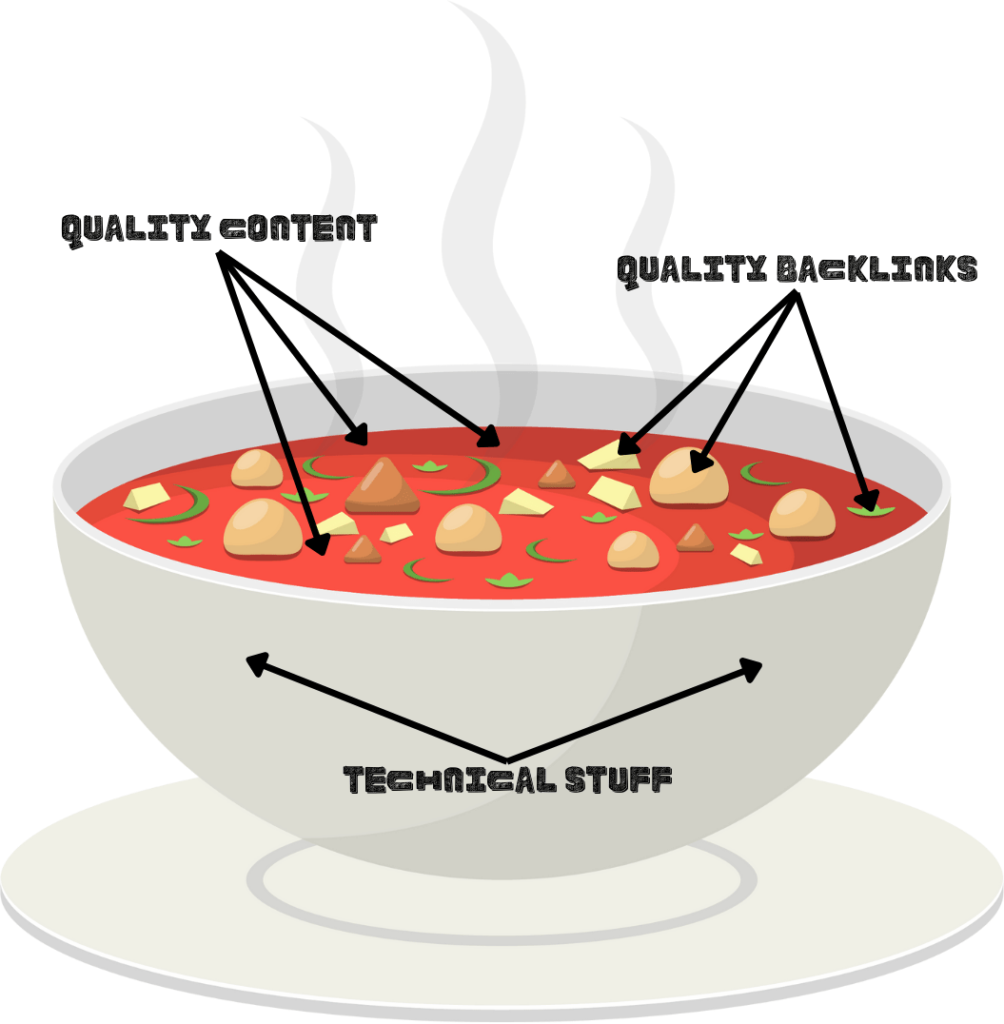
To simplify things, think of SEO Power Bowl
There are three key parts of SEO:
- Technical Stuff: The bowl itself represents the technical side of SEO (often called technical or on-page SEO). Without a solid bowl, there’s nothing to hold the soup.
- Quality content: The soup is your content. Without quality content, you can’t rank well—simple as that.
- Quality backlinks: The seasoning represents backlinks. Even if you have great content and a well-optimized site, you still need backlinks to build authority and perfect your SEO.
In the following sections, we’ll break down these aspects in more detail.
SEO Vocabulary
As you get into SEO, you’ll come across some common terms that describe different approaches or parts of SEO, such as:
- On-page SEO & off-page SEO
- Black hat SEO & white hat SEO
Though these terms may not be critical for day-to-day SEO, it’s helpful to know what they mean.
On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO
On-page SEO refers to everything you can do directly on your website to improve rankings, such as:
- Keyword research: Finding relevant keywords to target
- Content optimization: Making sure your content is high quality and relevant
- Title tag optimization: Ensuring titles accurately reflect your content
- Page performance: Improving page speed and user experience
- Internal linking: Linking to other relevant pages on your site
On-page SEO focuses on creating a great user experience while making it clear to search engines what your content is about.
Note: On-page SEO and technical SEO can sometimes be used interchangeably. However, technical SEO often refers to more behind-the-scenes aspects like page speed, while on-page SEO might focus more on content elements like title tags.
Off-page SEO, on the other hand, involves actions taken outside your website to improve rankings. The main goal here is building backlinks from other sites to show search engines that your site is valuable. Some ways to build backlinks include:
- Guest blogging
- Email outreach
- Broken link building
Off-page SEO is also linked to other marketing efforts, like social media and branding, which can indirectly help your SEO by boosting your site’s authority and trustworthiness.
Remember: A successful SEO strategy combines both on-page and off-page SEO.
White Hat SEO vs. Black Hat SEO
In old Western movies, white hats were worn by good guys, and black hats were worn by villains. In SEO, the terms represent ethical vs. unethical practices.
- Black hat SEO: These are unethical (and often spammy) tactics used to quickly improve rankings. While they might work in the short term, they often lead to penalties or a ban from search engines.
- White hat SEO: These are ethical SEO practices that follow Google’s guidelines. It’s a long-term approach where good rankings come from solid optimization, quality content, and a user-focused strategy.
Most SEO experts recommend sticking with white hat SEO, although there are debates around certain practices, like buying links.
FAQs About SEO
Can I Do SEO by Myself? Yes, you can! SEO isn’t easy, but it’s not impossible either. There are simple things you can do right away and more complex concepts that will take time to master. The real question is whether you’re ready to spend time learning SEO or prefer to hire a professional.
How Can I Learn SEO? To learn SEO, here’s what you should do:
- Read trustworthy sources
- Get hands-on experience
- Don’t be afraid to experiment
- Be patient (SEO is a long-term process)
Following the advice in this guide is a great way to start!
How Long Does It Take to Learn SEO? It depends. Learning the basics won’t take long—just a few weeks. However, mastering SEO can take months or even years of practice. Plus, SEO is always evolving, so you’ll need to keep learning to stay up to date with the latest trends and updates.
Do I Need SEO Tools? If you’re serious about SEO, using tools can give you valuable insights and save you time. Some essential tools every website owner should use include:
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics (or another traffic analysis tool)
- A keyword research tool (e.g., KWFinder)
- A backlink analysis tool (e.g., LinkMiner)
- A rank tracker (e.g., SERPWatcher)
Is SEO Dead? When people say “SEO is dead,” they’re usually talking about outdated, spammy tactics that tried to manipulate Google’s algorithm. Real SEO, however, is very much alive and continues to be a key part of digital marketing.
Chapter-2
Search engines
In this chapter, we’ll explore what search engines are, how they function, and the key factors that influence Google’s SEO rankings.
What Are Search Engines?
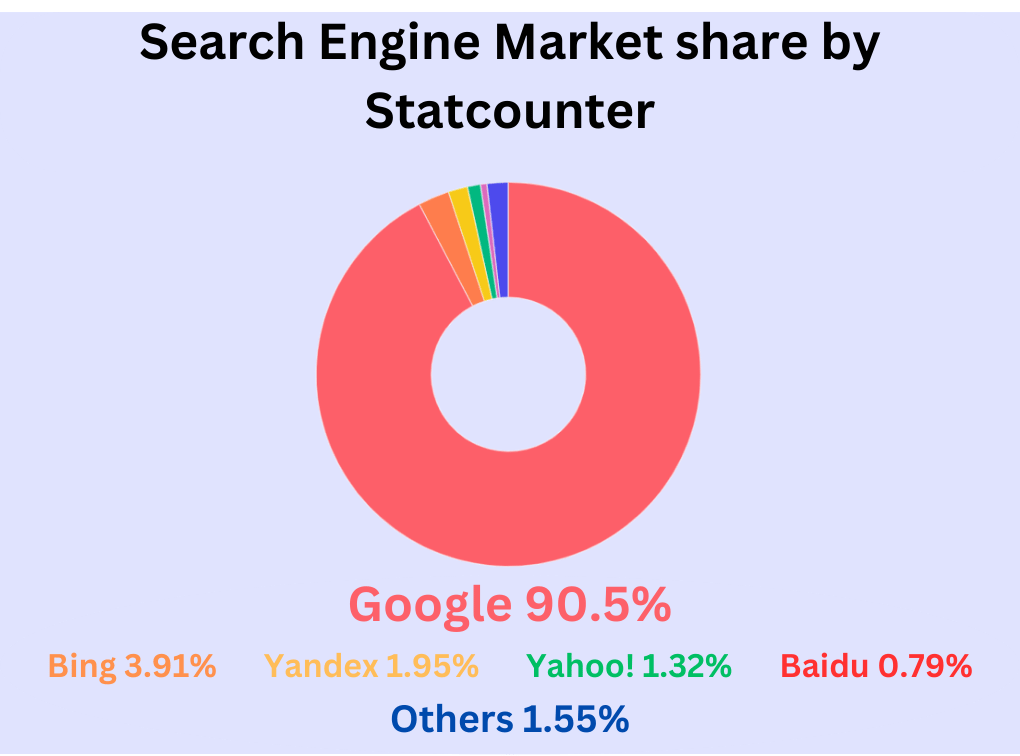
Search engines are online tools designed to help users locate information on the internet. The most prominent example is Google, which dominates the search engine market globally (according to Statcounter data).
The purpose of this guide is that when we refer to search engines, we primarily mean Google. Other search engines operate on similar principles, so optimizing your site for Google typically ensures compatibility with others.
How Search Engines Work
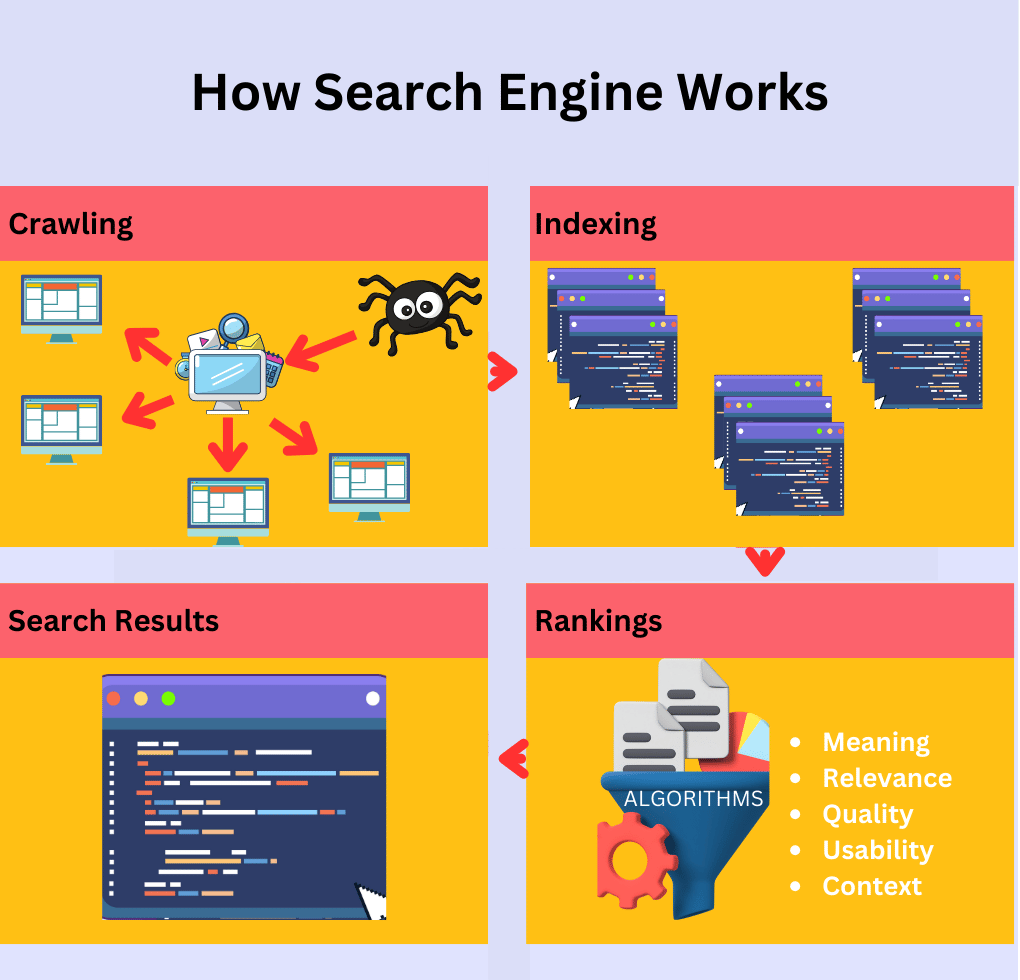
Search engines operate through a series of steps:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Selecting Results
- Displaying Results
Crawling: – This is the process where search engines continuously scan web pages across the internet. They use small programs known as crawlers or bots to follow hyperlinks, discover new pages, and detect updates to previously found pages. As Google Webmaster Trend Analyst Martin Splitt puts it:
“We start somewhere with some URLs and then follow links from there, crawling our way through the internet, page by page.”
Indexing: After a page is crawled, its information is indexed. The search engine analyzes and categorizes the content, storing it in a massive index akin to a digital library. This index allows the search engine to retrieve relevant information when users perform searches.
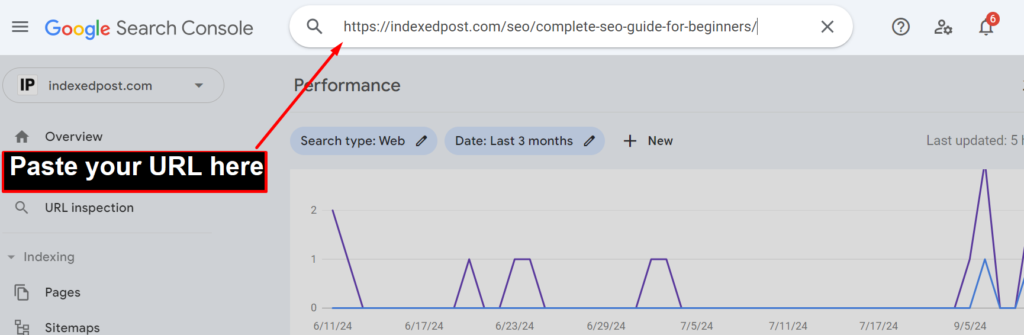
Tip: To check if your page has been crawled and indexed, use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console. It will show the last crawl date and any potential issues.
Selecting Results: When a user submits a search query, the search engine sifts through its index to present the most relevant results. This list of results is known as the Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
Google’s Search Algorithm
Google’s Search Algorithm encompasses various algorithms, machine learning systems, and technologies used to rank websites. It considers several factors to deliver the best results:
- Query Meaning: Understanding the user’s search intent.
- Page Relevance: Ensuring the page is relevant to the query.
- Content Quality: Evaluating the quality of the content on the page.
- Page Usability: Assessing factors like accessibility and readability.
- Context and Settings: Taking into account the user’s location, settings, and search history.
Google frequently updates its algorithms. While minor updates occur daily, significant core updates are rolled out a few times a year and are often announced publicly, creating buzz in the SEO community.
Reviewing key core updates like Panda, Penguin, and Hummingbird to understand how Google’s search algorithm has evolved can provide valuable insights.
Search Quality Raters
In addition to algorithms, Google employs human Search Quality Raters. These individuals evaluate search results and rate page quality based on publicly available guidelines. They do not directly influence rankings but provide data that helps refine the search algorithm. Pages dealing with significant topics affecting users’ well-being, known as YMYL (Your Money, Your Life) pages, undergo especially rigorous evaluations.
Ranking Factors
While Google keeps the specifics of its ranking calculations secret, many ranking factors are recognized within the SEO community. Although some factors are confirmed by Google, others remain speculative. It’s crucial to focus on factors with proven impacts while maintaining a balanced approach across all areas.
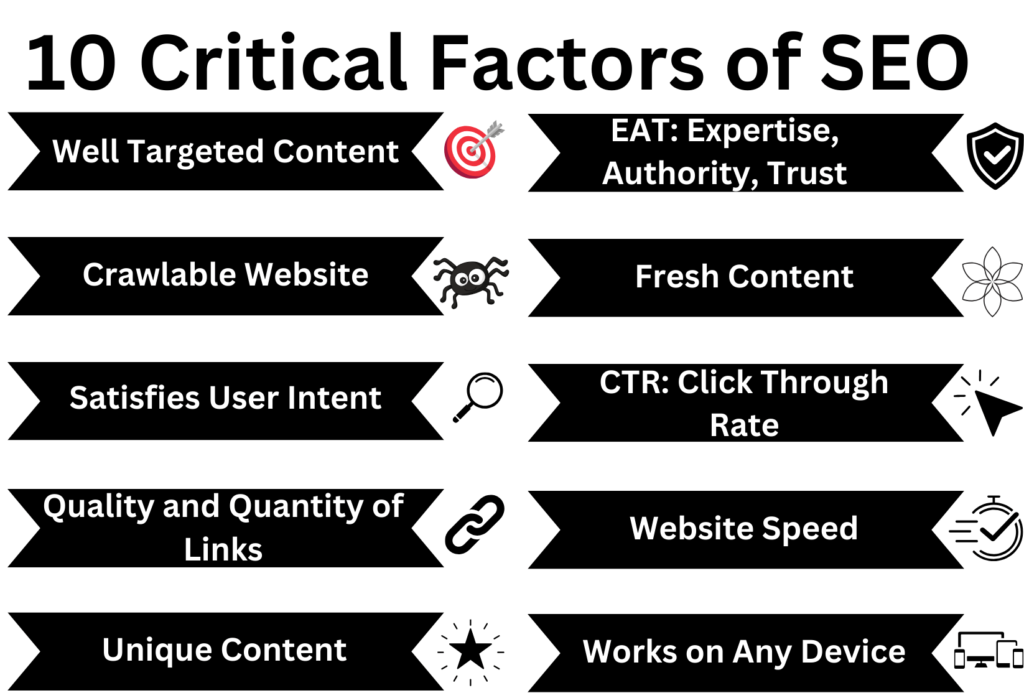
Key Ranking Factors:
- Well-Targeted Content: Create high-quality content tailored to what users are searching for.
- Crawlable Website: Ensure your site is easy for search engines to find.
- Quality and Quantity of Links: Gain backlinks from reputable sources to build authority.
- User Intent: Craft content that meets user needs and provides value.
- Unique Content: Avoid duplicate content to maintain originality.
- E-E-A-T: Demonstrate Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust.
- Fresh Content: Regularly update your content to keep it relevant.
- Click-Through Rate: Optimize titles and meta descriptions to improve CTR.
- Website Speed: Ensure fast loading times to prevent user frustration.
- Works on Any Device: Ensure your site functions well across all devices.
Additional Factors:
- Content depth
- Image optimization
- Topical authority
- Well-structured pages
- Social sharing
- HTTPS
Expert Insight: Kevin Indig, Director of SEO at Shopify, notes that SEO has evolved from focusing solely on fixed criteria to enhancing user experience. Google’s advancements in Information Retrieval, Natural Language Understanding, and Processing emphasize the importance of aligning SEO practices with user intent and overall experience.
For more in-depth information, continue reading Chapter 3 and beyond, where we delve deeper into specific SEO strategies, techniques, and best practices to enhance your website’s performance and visibility. Each chapter will build on the knowledge from previous sections, guiding you through the complexities of SEO to help you achieve better search engine rankings and a more effective online presence.
More chapters will come soon.